Julella lactea (A. Massal.) M.E. Barr
Syn.: Blastodesmia lactea A. Massal., Julella lactea (A. Massal.) M.E. Barr var. naegelii (Hepp) M.E. Barr, Polyblastia naegelii (Hepp) Trevis., Polyblastiopsis lactea (A. Massal.) Zahlbr., Polyblastiopsis naegelii (Hepp) Zahlbr., Sporodyction lacteum (A. Massal.) Trevis., Verrucaria lactea (A. Massal.) Garov., Verrucaria naegelii (Hepp) Nyl.
Non- or doubtfully lichenised.
Substrate: bark
Altitudinal range: from the mesomediterranean belt (potential vegetation: evergreen broad-leaved forests dominated by Quercus ilex) to the submediterranean/colline belt (potential vegetation: mixed deciduous forests dominated by Quercus and Carpinus)
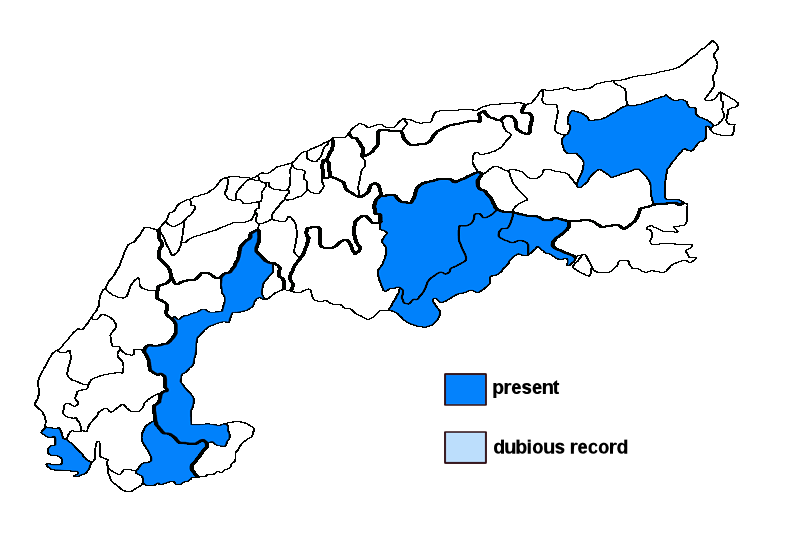
Note: a doubtfully lichenised species with an endophloeodic thallus indicated by white to grey patches, black perithecioid ascomata, the blackish-brown wall clypeus-like, 4-spored asci, anastomosing interascal filaments, and hyaline, muriform ascospores (30-36 × 12-15 µm) with 6-8 transversal septa and 2-3 longitudinal septa; on smooth bark, mostly of Fraxinus, most common in Southern Europe, on the foothills and in the valleys of the Southern Alps.
Austria: Steiermark; France: Alpes-Maritimes; Vaucluse; Italy: Friuli; Veneto; Trentino Alto Adige; Piemonte;