Physconia venusta (Ach.) Poelt
Syn.: Anaptychia subaquila (Nyl.) Kurok., Parmelia venusta Ach., Physcia pulverulenta (Wahlenb.) Fürnr. var. venusta (Ach.) Nyl., Physcia subaquila Nyl., Physcia venusta (Ach.) Nyl.; incl. Physcia amoena (Zahlbr.) Nádv.
Lichenised.
Substrate: bark
Altitudinal range: from the submediterranean/colline belt (potential vegetation: mixed deciduous forests dominated by Quercus and Carpinus) to the montane belt (potential vegetation: deciduous forests dominated by Fagus sylvatica and closed coniferous forests with Picea abies)
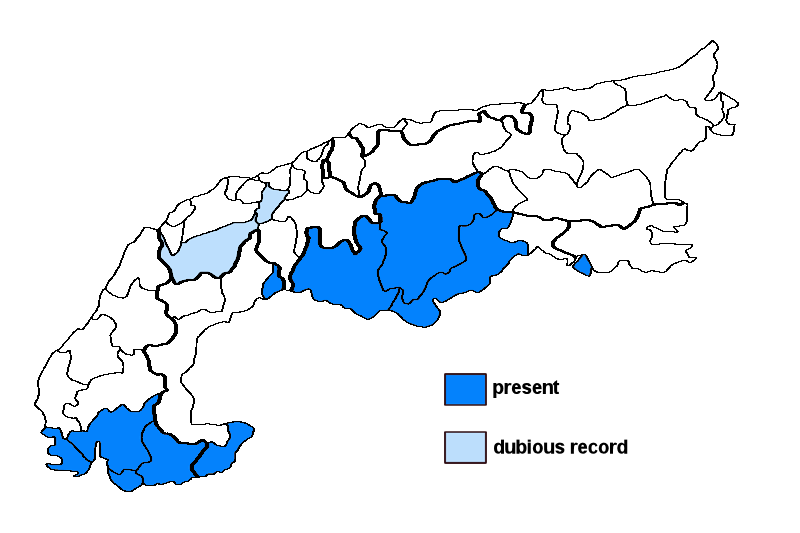
Note: one of the few lichens whose distribution is centered on the Mediterranean mountains, and one of the most abundant and typical lichens of the Central and South Italian humid beech forests, which is rare in the Alps. The forms called subaquila are worthy of further study: they differ in the black lower surface and the saxicolous growth, and could represent a good species.
Switzerland: ?Uri; ?Valais; France: Alpes-de-Haute-Provence; Alpes-Maritimes; Vaucluse; Var; Italy: Veneto; Trentino Alto Adige; Lombardia; Liguria; Slovenia: Trnovsky Gozd;